User Guide¶
Configuration¶
The config command of MotifScan manages the data paths of required
genome assemblies and motif sets (PFMs/PWMs).
The configurations include:
The default install location for genome assemblies
The default install location for motif sets
The path of every installed genome assembly
The path of every installed motif set
Config file¶
All the configurations are stored within a user specific config file which is
located at $HOME/.motifscanrc
Example:
[motifscan]
genome_dir = $HOME/.motifscan/genomes/
motif_dir = $HOME/.motifscan/motifs/
[genome]
hg19 = $HOME/.motifscan/genomes/hg19
[motif]
vertebrates = $HOME/.motifscan/motifs/vertebrates
The genome_dir and motif_dir entries set the default location for newly installed
genome assemblies and motif sets, respectively.
Under the [genome] section, each row records the path of an installed genome assembly.
Under the [motif] section, each row records the path of an installed motif set,
motif set PFMs file and PWMs file(s) are stored under the directory.
Default installation location¶
Newly installed genome assemblies are placed under $HOME/.motifscan/genomes/,
if you want to change it:
$ motifscan config --set-default-genome <path>
As for motif sets (PFMs/PWMs), the default path is under $HOME/.motifscan/motifs/,
you can also change it with command:
$ motifscan config --set-default-motif <path>
Data path modifiers¶
Whenever you newly install a genome assembly/motif set, the path of the genome/motif data directory is automatically saved in the configurations. If you later move the genome/motif directory to another place, you may have to modify the path manually.
Modify the path of an installed genome assembly:
$ motifscan config --set-genome <genome_name> <path>
Or modify the path of an installed motif set:
$ motifscan config --set-motif <motif_set> <path>
Tip
Please use the command motifscan config -h to see all the options.
Genome Subcommands¶
The genome command controls the genome assemblies used by MotifScan. MotifScan requires a sequences FASTA file and a gene annotation file (if available) for each genome assembly, users can either download them from a remote database or install directly with local prepared files.
Display installed genomes¶
The --list option of the genome command tells MotifScan to display all the
installed genome assemblies:
$ motifscan genome --list
Remote genome databases¶
MotifScan can access remote genome databases. UCSC is the only database MotifScan supports currently.
Display all available genome assemblies in the UCSC genome database:
$ motifscan genome --list-remote
Search for genome assemblies by a keyword:
$ motifscan genome --search <KEYWORD>
Install genomes from a remote database¶
To install a genome assembly directly from the UCSC genome database:
$ motifscan genome --install -n <genome_name> -r <remote_name>
The -r/--remote option specifies which remote genome is to be installed, and you
can give it a custom name with the -n/--name option, this genome name is used
to refer to the installed genome from then on.
Install genomes with local files¶
You can alternatively use local prepared genome data files to install a genome
assembly. Data files include a genome sequence FASTA file and a gene annotation
refGene.txt file.
$ motifscan genome --install -n <genome_name> -i <FASTA.fa> -a <refGene.txt>
Uninstall genomes¶
If a genome assembly is no longer used, you can choose to uninstall it:
$ motifscan genome --uninstall <genome_name>
Motif Subcommands¶
MotifScan only detects the binding sites (occurrences) of known motifs. Before scanning, the motif set should be installed with PFMs (Position Frequency Matrices) and built to obtain PWMs (Position Weight Matrices) and motif score cutoffs.
The motif command handles the motif sets of MotifScan. Basic operations are
listed as follows.
Display installed motifs¶
The --list option of the motif command tells MotifScan to display all the
installed motif PFMs sets:
$ motifscan motif --list
Remote motif databases¶
MotifScan can access remote motif databases. JASPAR CORE and JASPAR Collections
are supported currently.
Display all available motif PFMs set in the JASPAR CORE motif database:
$ motifscan motif --list-remote
Install motifs from a remote database¶
To install a motif PFMs set directly from the JASPAR CORE motif database:
$ motifscan motif --install -n <motif_set> -r <remote_name>
The -r/--remote option specifies which remote motif PFMs set is to be installed,
and you can give it a custom name with the -n/--name option, this name is used
to refer to the installed motif PFMs set from then on.
Install motifs with local files¶
You can alternatively use local prepared motif PFMs files to install a motif set. The PFMs file should follow the JASPAR motif format.
$ motifscan motif --install -n <motif_set> -i <pfms.jaspar>
Example:
>MA0006.1 Ahr::Arnt
A [ 3 0 0 0 0 0 ]
C [ 8 0 23 0 0 0 ]
G [ 2 23 0 23 0 24 ]
T [ 11 1 1 1 24 0 ]
Build motif PFMs into PWMs¶
After the motif PFMs set are installed, it needs to be built under a specific genome assembly to obtain PWMs and motif score cutoffs for motif occurrences. Since different assemblies have different genome contents, it is necessary to build the PFMs and get proper motif score cutoffs for every genome assembly you want to scan later.
$ motifscan motif --build -n <motif_set> -g <genome_name>
Motif score and cutoffs¶
Motif score¶
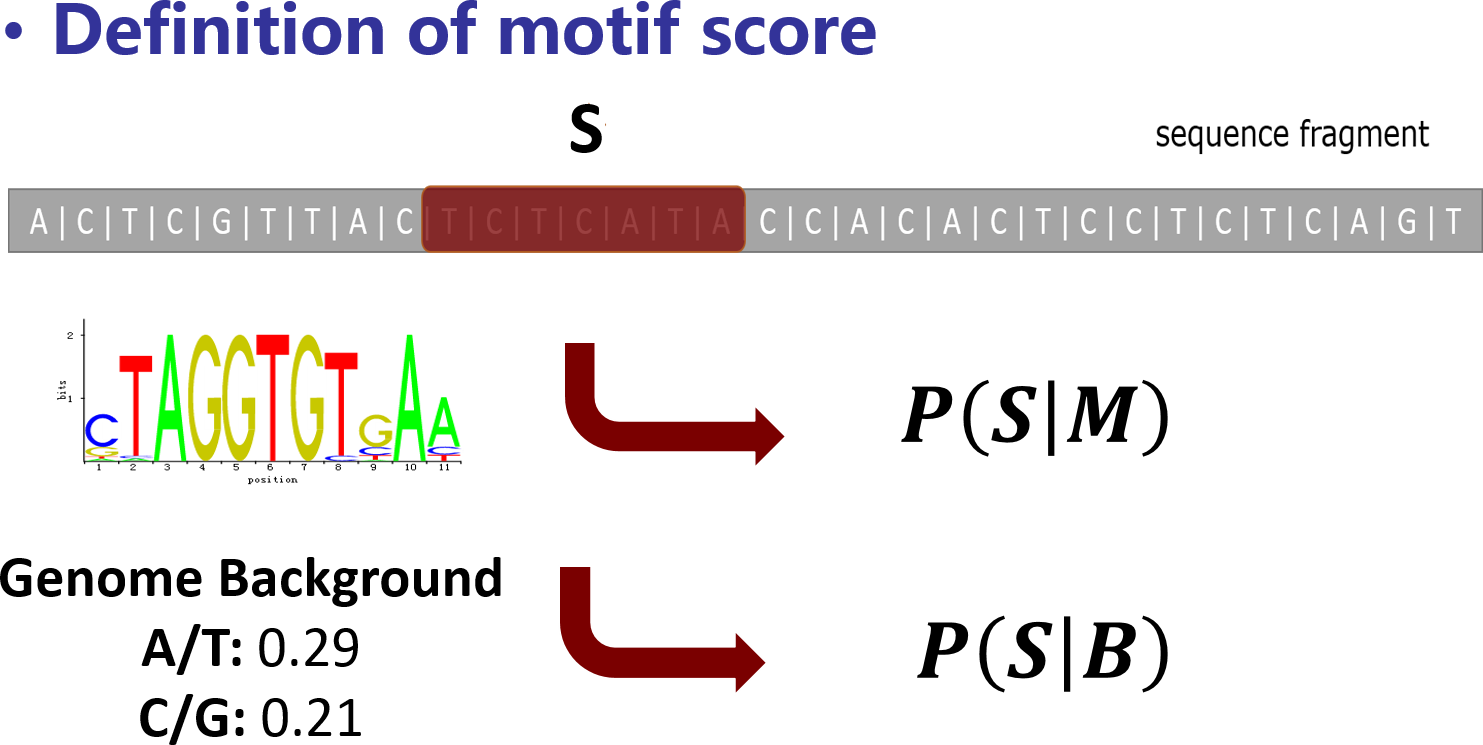
MotifScan uses motif score to measure the similarity between a sequence
S and the motif matrix M under specific genome background B.
The raw motif score is calculated as the log-scaled ratio of the probability to
observe S given the motif matrix M and the probability to observe S
given the genome nucleotides background B.
And motif score is defined as the normalized form of raw motif score
(divided by the maximal possible raw motif score).
Motif score cutoffs¶
The background distribution of the motif score is modeled by randomly sampling 10^6 times from whole genome background, and motif score cutoffs of different significance levels are determined according to the sampling distribution of the motif score.
By default, the sampling goes for 1,000,000 times and motif score cutoffs for P-value 1e-2, 1e-3, 1e-4, 1e-5 and 1e-6 are obtained.
Users can also trigger the --n-repeat option to perform the whole sampling procedure
described above for multiple times and use the averaged cutoffs as final cutoffs.
Uninstall motifs¶
You can choose to uninstall no longer used motif set:
$ motifscan motif --uninstall <motif_set>
Scan Command¶
This main command invokes to scan the sequences of user specified input genomic regions and detect the occurrences for a set of known motifs. After scanning the input regions, an optional motif enrichment analysis is performed to check whether these motifs are over/under-represented compared to control regions (can be random generated or user specified).
Basic Usage¶
The basic usage is to specify the genomic regions to be scanned, the genome name, the motif set to scan for, and the output directory.
$ motifscan scan -i <regions.bed> -g <genome_name> -m <motif_set> -o <output_dir>
Regions file format¶
MotifScan supports multiple formats for the genomic regions file, you can use
-f option to specify the format, see Genomic Regions Format for more details.
Scanning Options¶
- -p
P value cutoff for motif scores. Default: 1e-4
- --loc
If specified, only scan promoter or distal regions.
- --upstream
TSS upstream distance for promoters. Default: 4000
- --downstream
TSS downstream distance for promoters. Default: 2000
- -w, --window-size
Window size for scanning. In most cases, motifs occur closely around the centers or summits of genomic peaks. Scanning a fixed-size window is often sufficient to detect motif sites and unbiased for the enrichment analysis. If set to 0, the whole input regions are included for scanning. Default: 1000
- --strand
Enable strand-specific scanning, defaults to scan both strands.
Motif Enrichment Analysis¶
After scanning the input genomic regions, MotifScan will randomly generate some control regions to perform a motif enrichment analysis. The random generated regions are controlled to have similar genomic locations (promoter/distal, distance to nearest TSS etc.) with the input regions. Users can optionally specify a set of custom control regions for the motif enrichment analysis.
- --no-enrich
Disable the enrichment analysis.
- --n-random N
Generate N random control regions for each input region. Default: 5
- --seed SEED
Random seed used to generate control regions.
- -c FILE
Use custom control regions for the enrichment analysis.
- --cf
Format of the control file. Default: bed
Speed up with multiple threads¶
Even through the scanning functions are implemented in C extensions to improve the speed,
the scanning procedure still takes a while especially when the input genomic regions is large.
Try to specify -t options to use multiple threads to make it faster if your machine allows.
Optional output files¶
- --site
If set, report bed files with the positions for detected motif sites.
- --plot
If set, plot the distributions of detected motif sites.
Genomic Regions Format¶
Note
The score attribute is required if you specify the --plot option.
BED3-summit¶
A customized BED format named as BED3-summit is also supported, the first 3
columns is the same as BED format, and the 4th columns should be the absolute
summit position.
Note
This is not a standard format but a variant of BED3 for convenience.
MACS¶
MACS (version 1.x) xls format is supported, the chrom, start, end,
summit and -10*log10(pvalue) columns are used.
MACS2¶
MACS2 xls format is supported, the chrom, start, end, summit
and -log10(pvalue) columns are used.
Warning
This is not compatible with the broad mode of MACS2.
narrowPeak¶
ENCODE narrowPeak format is supported, the columns chrom, start, end
and score are used. If the 10th column is available, MotifScan uses it as the
summit coordinate.
Output Files¶
motif_sites_number.xls
This file summarizes the numbers of detected motif sites (occurrences) for the input genomic regions. The first 3 columns specify the genomic coordinates (1-based) and additional columns report the numbers of detected motif sites within each input region.
motif_sites_score.xls
This file reports the maximal motif scores of motifs for each input genomic region. If a motif have no sites detected within a specific genomic region, the corresponding value will be reported as NA. Coordinates are also 1-based.
motif_enrichment.xls
This file is written when the motif enrichment analysis is performed.
Motif: Motif name.
Num_input_regions: The number of input genomic regions which have at least 1 motif site.
Num_control_regions: The number of control genomic regions which have at least 1 motif site.
Fold_change: Ratio between the fraction of input regions with motif site(s) and the fraction of control regions with motif site(s).
Enriched_P_value: P value of single-sided fisher exact test, alternative=’greater’.
Depleted_P_value: P value of single-sided fisher exact test, alternative=’less).
Corrected_P_value: Bonferroni corrected P value (the smaller one between enriched and depleted).
motif_sites/<motif_name>_sites.bed
These files reports the detailed positions of all detected motif sites.
Note
These files are only generated when the --site option is enabled.
plot/<motif_name>_sites_distributions.pdf
These figures shows the genomic position distributions of detected motif sites relative to the summits or centers of the input genomic regions.
Note
These files are only generated when the --plot option is enabled.
If -w is 0, input genomic regions are required to have the same length.
plot/<motif_name>_sites_enrichment.pdf
These figures shows the enrichment (fold change) of detected motif sites number
between input and control genomic regions. Input genomic regions are ranked by the
score attribute.
It is helpful when you want to check the correlation between a motif and certain attribute of the input genomic regions. For example, if the score values represent the ChIP-seq intensities, you can inspect if a motif is more enriched (appears more frequently) at genomic regions with higher ChIP-seq signals.
Note
These files are only generated when the --plot option is enabled and motif
enrichment analysis is performed. Input genomic regions are required to have the
score information, otherwise MotifScan will not report these figures.